SBS-Factory/en
Contents
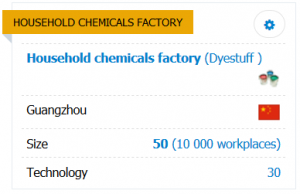
FACTORY
Specialization - the current specialization of the enterprise, which determines the type of products to be produced.
Size - the size of the subdivision, determining its maximum production capacity. It is indicated in basic units - blocks (the corresponding number of work places is indicated in brackets).
Technology - the current technological level of the subdivision, which determines quality and quantity of manufactured products and defines requirements for the quality of equipment and the level of qualification of employees.
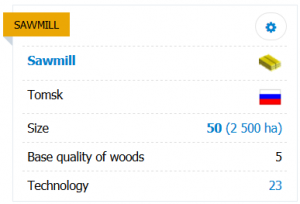
SAWMILL
Size (cutting area) - the size of the subdivision, determining its maximum production capacity. It is indicated in basic units - blocks (the corresponding forest area is indicated in brackets).
Base quality of woods - is the basic quality of wood in the home town of the sawmill. Not subject to change, gradation from 1 (bad) to 5 (good). This indicator, along with technology, affects the final quality of wood produced at the Sawmill.
Technology - the current technological level of the subdivision, which determines the quality and quantity of manufactured products and defines requirements for the quality of equipment and the level of qualification of employees.
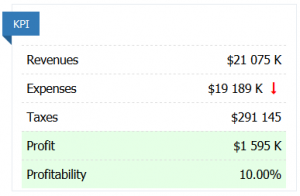
KPI
Revenues - revenue of the unit for the last turn for the sale of goods and services.
Expenses - all expenses of the unit that were incurred in the last turn.
Taxes - taxes paid by the unit. Details on tax burden calculations are found in “Financial report” > “Income Statement”. Full information on the principles of taxation can be found in the article Taxes.
Profit - cash flow from operations for last turn (difference between Revenues and Expenses).
Profitability - the profitability of the unit.
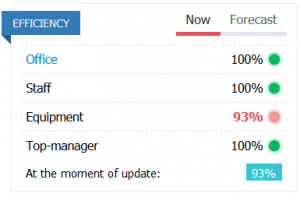
EFFICIENCY
Efficiency of the Office - the efficiency of the managing office of the region, where the subdivision is located.
Efficiency of the staff - is determined by the correspondence of the qualification level of the staff to the required value. Requirements for the level of qualification of personnel are determined by the quality of the installed equipment. An increase in the qualifications of personnel above the required level does not affect the performance of the enterprise, but increases the burden on the manager, as a result of which his efficiency may decrease. To maintain the optimal ratio, you can use the Human Resources Department service, which automatically sets the required value for personnel qualifications through wage adjustments.
Efficiency of Equipment - is determined by the correspondence of the quality of the installed equipment to the required value, and wear and tear. Requirements for the quality of equipment are determined by the level of technology installed in subdivision. An increase in the quality of equipment above the required level does not affect the performance of the enterprise, but imposes increased requirements on personnel.
The efficiency of a Top-manager - the efficiency of management of Top-manager. Depends on the correspondence of the Top-managers skill “Production” to the qualifications of the staff in all similar (using this skill) subdivision of the company as a whole.
Production efficiency (at the time of turn) is the main indicator of how well the production is organized. One hundred percent efficiency speaks of the optimal level of correlation between the size of the enterprise, the technological level, the quantity and quality of equipment, the number and qualifications of personnel, the qualifications and loading and efficiency of Top-manager. Low efficiency leads to a decrease in production volume and product quality, as well as a growing proportion of defective products. All this leads to an increase in the cost of production, which means a loss of competitiveness and losses.
Final efficiency depends on four indicators:
- Office efficiency
- Staff efficiency;
- Equipment efficiency;
- Top-managers "Production" skill level
EMPLOYEES AND SALARY
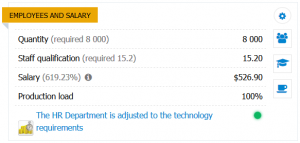
Quantity - the current number of employees in the subdivision.
Staff qualification - the current qualification level of employees (in addition, the city average qualification value and the required value determined by the quality of equipment are indicated in brackets). Excessive qualification level of employees does not lead to improvement of production parameters and at the same time increases requirements for the level of “Production” skill of Top-manager. Qualification indicator can be raised by training staff, or by a change in salary (the effect of a change in salary is visible immediately, you do not need to wait for next turn).
Salary of one employee - weekly salary of one employee. The average salary of employees of this type of units in the city is indicated in brackets (each type has its own coefficient).
EQUIPMENT
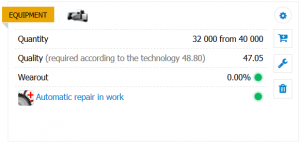
Quantity - the amount of equipment installed. Along with the number of workers determines the load of the enterprise and its current production potential in terms of output.
Quality - the current quality of installed equipment. Higher-quality equipment than required by technology does not affect production parameters.
Wear and tear - the current degree of equipment wear and tear. A high degree of wear and tear will negatively affect the overall efficiency of the equipment, which leads to a decrease in the quality and quantity of products. Even at 100% efficiency of the equipment, the volume of output is still reduced in proportion to wear and tear. The standard service life of machine tools and sawmills is 10 virtual years (weekly base wear and tear is approximately 0.19%). In addition, the quality of the equipment itself affects wear and tear (it decreases by 1% per quality unit) and the ratio of the required and current qualifications of the personnel working with it (workers with less than required qualifications wear out equipment faster than more intelligent employees). Worn out equipment directly affects its efficiency. Since depreciation is calculated as a percentage, partial wear and tear of a piece of equipment is possible - in this case, the marker “+1” is added to the value of the worn-out amount of equipment. Partially worn out equipment can be fixed only by fully replacing it.
TOP MANAGER
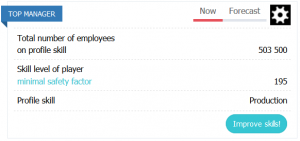
The total number of employees on profile skill - is the total number of employees of all subdivisions of this type in the company. It affects the efficiency of the Top-manager.
Skill level of player - the current level of “Production” skill. Determines the maximum possible number and qualification of employees without loss of efficiency both in this particular unit and in all subdivisions of the company as a whole (an additional hint about the stock of the current level compared to the minimum required can be indicated in brackets, minimum - 0-25%, normal - 25-50%, good 50-100%, excellent - more than 100%).
SUPPLY
Manufacturing enterprises depend on the supply of raw materials. Various products can be used as raw materials: minerals, agricultural products, or materials. The need for raw materials for the production of a particular product is determined by the technological scheme of production.
Raw materials can be purchased at the enterprises of any company in the entire playing space. In addition, some strategic types of raw materials can be purchased from independent suppliers in the global market. Your company can buy raw materials from various suppliers of different quality and at different prices at the same time. The choice of one or another supplier depends on the availability of a sufficient amount of raw materials in its warehouse, the quality of raw materials, as well as the prices established by supplier, as well as the geographic location of the supplier. Some suppliers may have restrictions in their sales policy, so not all manufacturers of this type of raw material will sell it openly.
When purchasing raw materials, it is necessary to determine the volume of a batch purchased from each of the suppliers per week. The volume of supplies of raw materials should ensure the continuity of production, therefore it is often necessary to have some reserve in the warehouse of raw materials in case of interruptions in the work of suppliers or changes in their sales policies. However, the accumulation of too much stock of raw materials can be unprofitable, since it leads to a freezing of capital in assets that do not bring profit, as well as an increase in storage costs.
Supply - the activity of supplying the necessary raw materials and goods for the successful operation of the enterprise (selling goods in a store or manufacturing products in factories, mills and farms).
In order to supply the subdivision with raw materials (goods), contract is necessary in order for one of the suppliers to provide a required amount of raw materials (goods). There are two ways to place an order for supply.
First way:
- Go to the “Supply tab”
- Go to the “Order” for list of suppliers (there click "add supplier button")
- The list of suppliers displays: the name of the company, the amount of resources in its warehouse and the number of free (available for order) resources. You can also find out the cost of a resource (separately - price, delivery cost and amount of duties, total cost) and its quality. You can sort the list by any of the categories and find the company with the lowest price or the largest number of available resources.
You can also use vendor filtering (click "advanced filter"). Filtering will allow you to quickly discard enterprises that no longer have available resources to fulfill your orders, as well as companies that offer products of insufficient quality.
The second way to order for supply is convenient if you place a supply order for supplier, that belonging to you. For example, if you have a mill, a bakery and shops, then you can go to the "sales" tab and click on the button (green car) to the left of the manufactured goods (flour), select your bakery and shops and indicate the delivery quantity for each. Similarly, by entering the bakery, you can specify the amount of bread delivery for each of your stores without going to the management pages of the stores themselves.
The raw materials ordered by you will automatically arrive at the enterprise’s warehouse every turn if there is sufficient quantity available for ordering in the supplier’s warehouse. A break in supply is possible both on the part of the buyer (triggering a filter by quality or price, or manual contract break), and on the part of the supplier (changing the marketing policy of sales, manual break). Also note that your order can be moved up or down in the shipping queue. The queue is formed manually by the supplier, and you can contact him with a request to stabilize and guarantee the supply of raw materials to your enterprise.
The filter for cutting off the supply of products makes it possible to carry out quality control of the parameters of the purchased raw materials price and quality wise. Cut-off of deliveries at a price occurs the next turn after the supplier changes the price above the established threshold. In the course of the price change, the products are delivered at the OLD price, and a color notification about the price change appears in the supply window. The price cut-off setting has 6 percent values (5%, 10%, 20%, 50%, 100%, never) and an absolute value that can be set. When the price rises by the set value (by 5%, by $ 100), the algorithm is triggered.
Quality cut-off occurs when the quality of the delivered products decreases below the established level. If the supplier’s proposal does not meet the specified quality limits, then the contract is not processed for transaction, but it does not break and is not reset. However, these contracts (which do not satisfy the quality conditions) do not affect the displayed quantity of available goods for other buyers.
The restriction on the minimum quality of the purchased goods may operate in parallel with price limits.
SALE
Product sales are recorded once a day during game data processing. Sale of products occur if one of the buyers left orders for the purchase of products and the buyer had enough money to pay for the entire batch of the order. The exception is the sale of equipment and animals. These purchases are made online, the goods and money are transferred instantly, at the time of the conclusion of the contract by the buyer.
In order for products to be sold, it is imperative to set a price and select a type of sales. There are five options for organizing product sales:
- “Not for sale” - stop selling products (used for temporary preservation of products, for example, in case of insufficiently favorable market conditions);
- “To any customer” - to sell products without restriction to all comers (the most commonly used type of sale). In this case, the products will be available for order to all potential buyers;
- “Only to certain companies” - to sell products only to the enterprises of the selected company. In this case, third-party customers will not be able to order products;
- “Only to my company” - to sell products only to enterprises of their own company. In this case, the products are not available to buyers of any other companies;
- “Only to members of the corporation” - sell products only to members of the corporation of which the company is a member of. In this case, products for buyers of any other companies are not available.
By default, the price is set to zero and the “Not for sale” mode.
On the tab of the "Sales" unit, not only the sales parameters of the products are displayed, but also the current list of customers who placed the order. If there are no orders for your products, it is possible that its price is too high, or quality and (or) brand values are to low. You can also change the shipment queue, giving priority to certain contracts.
TECHNOLOGIES
All manufacturing enterprises are characterized by a certain technological level. The level of technology affects the productivity of workers and product quality. The higher the level of technology, the higher labor productivity and higher quality. On the other hand, the technological level imposes higher requirements on the qualifications of workers and the quality of equipment. In addition, with the growth of the technological level, energy costs are rising.
There are 2 ways to introduce a technology: by purchasing the technology itself (or by researching it) and then installing it on any of the subdivision of the corresponding type, or by purchasing a one-time right to install the technology (license) for a particular subdivision. The payment for raising the technological level of an enterprise by purchasing the technology itself consists of two parts: payment for the purchase of technology and payment for implementation. Technology is purchased once by the company, that is, when the technological level of another subdivision of the same type is raised, the company pays only for the introduction of the technology.
Another possibility of introducing technologies in only one division is the creation of a sales market for so-called licenses, as an alternative to the technology market, bought by the players for introduction in all subdivisions of a certain type. For representatives of small and medium-sized businesses, the purchase of licenses is an alternative for buying technology in the case when the player does not have the means to purchase technology, or when the player has a small number of enterprises in one particular industry and the purchase of technology is not economically justified. For more information about the procedure for acquiring licenses, see the Science section.
When you purchase a high-tech subdivision from another player, its technology does not become the property of the company, although it is used at the acquired subdivision. Therefore, if you want to establish this technological level at your other subdivisions, you will again have to pay for both the purchase of the technology and its implementation.